Currently unable to deploy Azure database server resources. This is a temporary, tested workaround.
(edit Apr-2021) For a brief time, some Azure subscriptions configured for education had very limited capability to configure and deploy Azure SQL Server (PaaS) instances. Azure training documents reference the benefits of using Azure SQL database as a service in contrast to creating a virtual machine, then installing and configuring and managing the system, firewall(s) and a SQL server instance.
Create VM use Windows 10 From the Size diaglog, sort by cost and select the minimum configuration. This is adequate for student database requirements. This setting may be unsatisfactory for running any developer or activities beyond a single SQL Server instance. We can scale up if we need to.
This estimated cost is very reasonable, but can be reduced further by using Linux instead of Windows 10.
Enable RDP port, review and deploy.
note: the first deployment failed. steps were repeated using SqlDbWinVM1 and assigned a new IP address: 13.78.132.132. Results will be the same but the actual machine instance may not match the screenshots
From the Networking settings, Add Inbound Port Rule to enable inbound SQL TCP port traffic (typically: 1433)
Connect to VM using Remote Desktop (on port 3389), enter credentials and accept security certificate.
The first connection on startup to the Windows machine may take some time.
Download and install SQL Server. I used Developer Edition for this demonstration
After the installation completes, open Sql Server Configuration Manager and enable TCP/IP protocol.
Run SQL Configuration
And restart the SQL Service to enable the changes
Configuring SQL Server can be done from the command line, but SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) will simplify this task.
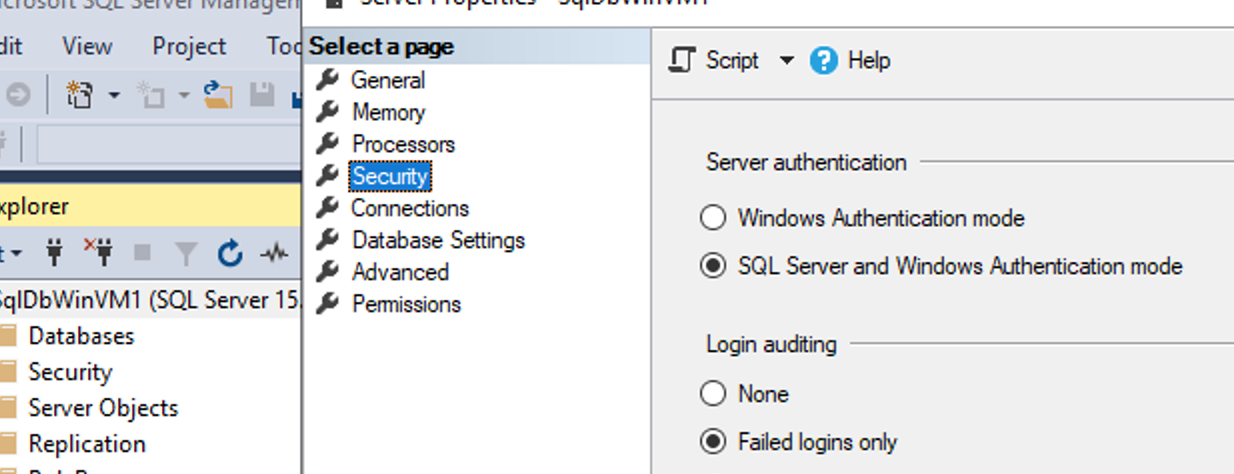
Connect to the SQL Server (with SSMS), using Windows Authentication and setup SQL Authentication
Add and configure Sql Login
Setup SQL Server to use SQL Authentication
Windows also installs a Firewall by default and the port exception needs to be added there as well.
Set port 1433 to allow connections and save changes
Log out of the VM, leaving it running (or simply close the remote desktop session).
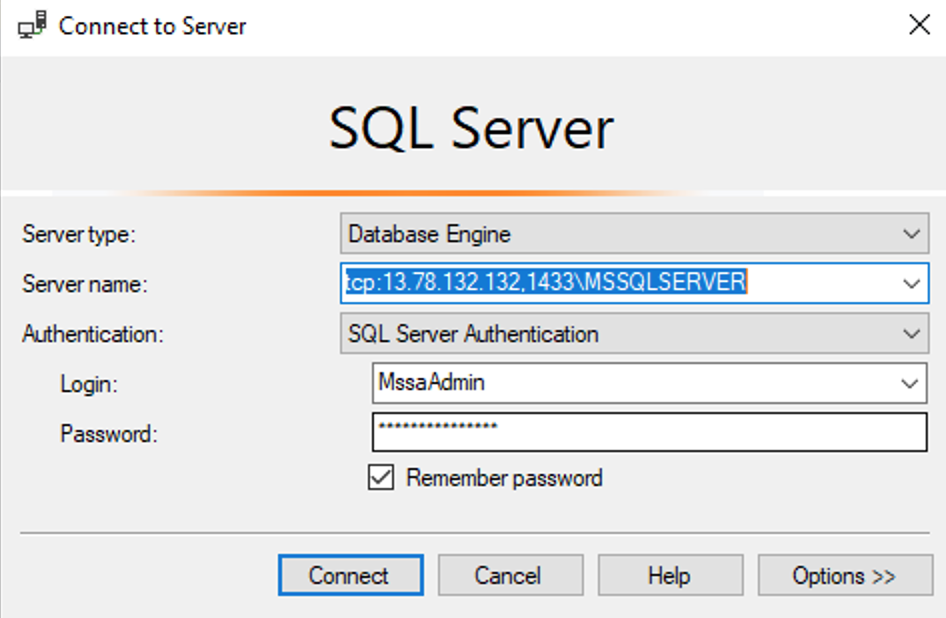
Test the remote connection. tcp:IP,port \ ServerName
tcp(colon) ipaddress(comma) port_number